Jetpack Compose provides OverscrollEffect in androidx.compose.foundation to create customizable overscroll effects.
While this works well in many scenarios, integrating it with lazy layout managers like LazyColumn can be less
straightforward. A more robust alternative involves using NestedScrollConnection to create a custom overscroll modifier.
However, this requires overriding methods like onPreScroll, onPostScroll, and onPreFling, which adds complexity.
Interestingly, Modifier.pullRefresh, while designed for pull-to-refresh functionality, bears similarities
with an overscroll modifier, albeit limited to one direction.
In this blog, we’ll creatively repurpose it to build a custom overscroll modifier and
craft an interactive header as shown below:

To start, we’ll design a curved path for the header. The function below defines a quadratic Bezier curve from
the bottom left to the bottom right:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
private fun composeCurvedPath(
width: Float,
height: Float,
path: Path,
curveRatio: Float = 1f,
) {
path.reset()
// Move to the bottom left corner
path.moveTo(0f, height + 1)
// Define a quadratic bezier curve from bottom left to bottom right
path.quadraticTo(
x1 = width / 2, // Control point X
y1 = (height - height * curveRatio), // Control point Y
x2 = width + 1, // End point X
y2 = height + 1, // End point Y
)
// Close the path back to the starting point
path.lineTo(0f, height + 1)
path.close()
}
|
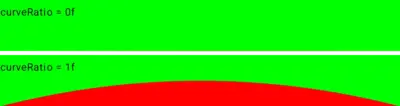
The curveRatio determines the curve’s shape. A value of 1 creates a full curve, while 0 flattens it into a straight line.
Using this path, we’ll create a composable that draws the path with a solid color:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
/**
* This view draws a curved arc
*
* @param color: the filled color of the curve
* @param curveRatio: a ratio of 1 means a complete curve, and a ratio of 0 means a flat line
*/
@Composable
private fun CurvedBackground(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
color: Color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.surface,
curveRatio: Float = 1f,
) {
Box(
modifier = modifier.drawWithCache {
val hasValidCurveParams = size.minDimension > 0f
if (!hasValidCurveParams) {
onDrawWithContent {}
} else {
val paint = Paint().apply {
isAntiAlias = true
this.color = color
style = PaintingStyle.Fill
}
val path = Path()
composeCurvedPath(
width = size.width,
height = size.height,
path = path,
curveRatio = curveRatio,
)
onDrawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
canvas.drawPath(path, paint)
}
}
}
}
)
}
|
Here is how it looks using a green background color and a red fill color with a curveRatio of 0 and 1 respectively:

This allows us to create a visually appealing curved header by putting the curve at the bottom of an image:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
@Composable
fun CurvedImage(
@DrawableRes imageRes: Int,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
) {
Box(
modifier = modifier
.background(MaterialTheme.colorScheme.surface)
.clipToBounds(),
) {
Image(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
painter = painterResource(imageRes),
contentDescription = null,
contentScale = ContentScale.FillWidth,
)
CurvedBackground(
modifier = Modifier
.align(BottomCenter)
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(50.dp),
curveRatio = 1f,
)
}
}
|

Let’s look into Modifier.pullRefresh:
1
2
3
4
|
fun Modifier.pullRefresh(
state: PullRefreshState,
enabled: Boolean = true
) = pullRefresh(state::onPull, state::onRelease, enabled)
|
The Modifier.pullRefresh relies on an associated PullRefreshState. Let’s simplify it into an OverscrollState
tailored to our use case:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
|
/**
* A state object that can be used in conjunction with [overscroll] to add overscroll
* behaviour to a scrollable component.
*
* Provides [progress], a float representing how far the user has over scrolled as a percentage
* of the [threshold]. Also provides the over scrolled [offset].
*
* Should be created using [rememberOverscrollState].
*/
@Stable
class OverscrollState internal constructor(
private val animationScope: CoroutineScope,
private val threshold: Float,
) {
private val offset get() = position
val progress get() = position / threshold
private var position by mutableFloatStateOf(0f)
private var distancePulled by mutableFloatStateOf(0f)
internal fun onPull(pullDelta: Float): Float {
val newOffset = (distancePulled + pullDelta).coerceAtLeast(0f)
val dragConsumed = newOffset - distancePulled
distancePulled = newOffset
position = (distancePulled * DRAG_MULTIPLIER).coerceAtMost(threshold)
return dragConsumed
}
internal fun onRelease(velocity: Float): Float {
animateIndicatorTo(0f)
val consumed = when {
// We are flinging without having dragged it down first (for example a fling inside
// a list) - don't consume
distancePulled == 0f -> 0f
// If the velocity is negative, the fling is upwards, and we don't want to prevent the
// the list from scrolling
velocity < 0f -> 0f
// It's already dragged down, and the fling is downwards - consume everything
else -> velocity
}
distancePulled = 0f
return consumed
}
// Make sure to cancel any existing animations when we launch a new one. We use this instead of
// Animatable as calling snapTo() on every drag delta has a one frame delay, and some extra
// overhead of running through the animation pipeline instead of directly mutating the state.
private val mutatorMutex = MutatorMutex()
private fun animateIndicatorTo(offset: Float) = animationScope.launch {
mutatorMutex.mutate {
animate(
initialValue = position,
targetValue = offset,
) { value, _ ->
position = value
}
}
}
}
internal object OverscrollStateDefaults {
/**
* The distance pulled is multiplied by this value to give us the adjusted distance pulled,
* which is used in calculating the offset
*/
const val DRAG_MULTIPLIER = 0.5f
}
|
Since we only need the progress property, all unrelated logic has been removed.
With this simplified state object, we can replicate the behavior of Modifier.pullRefresh
using our custom OverscrollState instance:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
/**
* Adds overscroll behavior to a scrollable component.
*/
fun Modifier.overscroll(
state: OverscrollState,
enabled: Boolean = true,
) = pullRefresh(state::onPull, state::onRelease, enabled)
|
Next, we need to provide a way to create a state object similar to rememberPullRefreshState but way simpler:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
/**
* Creates an OverscrollState that is remembered across compositions.
*/
@Composable
fun rememberOverscrollState(): OverscrollState {
val scope = rememberCoroutineScope()
val thresholdPx = with(LocalDensity.current) { OverscrollStateDefaults.THRESHOLD.toPx() }
val state = remember(scope) {
OverscrollState(
animationScope = scope,
threshold = thresholdPx,
)
}
return state
}
internal object OverscrollStateDefaults {
/**
* The maximum allowed over scroll distance
*/
val THRESHOLD = 80.dp
}
|
The OverscrollState can be easily passed into CurvedImage as shown below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
@Composable
fun CurvedImage(
@DrawableRes imageRes: Int,
overscrollState: OverscrollState = rememberOverscrollState(),
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
) {
Box(
modifier = modifier
.background(MaterialTheme.colorScheme.surface)
.clipToBounds(),
) {
Image(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.graphicsLayer {
scaleX = 1 + overscrollState.progress
scaleY = 1 + overscrollState.progress
},
painter = painterResource(imageRes),
contentDescription = null,
contentScale = ContentScale.FillWidth,
)
CurvedBackground(
modifier = Modifier
.align(BottomCenter)
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(50.dp),
curveRatio = 1 - overscrollState.progress,
)
}
}
|
The overscrollState.progress dynamically scales up the header image during over-scrolling
while flattening the curve proportionally.
With everything in place, we can now apply the custom modifier to a scrollable screen:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
@Composable
fun ScrollableScreen(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
) {
val overscrollState = rememberOverscrollState()
Scaffold(
modifier = Modifier
.overscroll(overscrollState)
.fillMaxSize()
) { innerPadding ->
LazyColumn(Modifier.padding(innerPadding)) {
item {
CurvedImage(
modifier = modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
overscrollState = overscrollState,
imageRes = R.drawable.img1,
)
}
repeat(20) {
item {
Text(
modifier = Modifier.padding(8.dp),
text = "Item $it",
)
}
}
}
}
}
|
With just a few lines of code, we’ve successfully integrated a custom overscroll effect and
a visually appealing curved header into our app.